Summary
The actin cytoskeleton is vital for a number of biological processes, including morphogenesis, motility, polarity establishment, and modulation of mechanical stress. These various tasks are performed by precise spatio-temporal control of actin polymerization/depolymerization dynamics. However, little is known about the regulatory mechanisms of actin assembly in these processes in vivo. We use a multi-disciplinary approach that combines genetics, biochemistry, histology, and pharmacology to study these problems from the molecular to organism level.
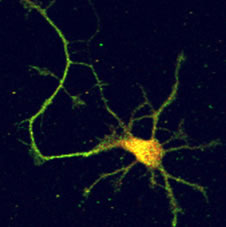
We are also interested in understanding the role of insulin signaling in the brain. Recent studies have revealed that insulin signaling is involved in cognitive functions under physiological and pathological conditions. We are addressing this issue from the unique standpoint that insulin is synthesized within the brain.
Research Projects
- Actin assembly mechanisms
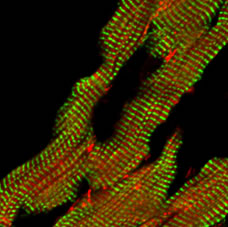
- Actin dynamics in cardiomyocytes and non-muscle cells
- Insulin signaling in the brain
Lab Techniques

- Basic molecular biology techniques
- Basic techniques for mammalian cell culture
- Maintenance and handling of genetically modified mice
- Expression and purification of recombinant proteins
- Primary culture of cardiomyocytes and neurons
- Morphological and histological observation techniques
Publications
- Nemoto T, et al. New insights concerning insulin synthesis and its secretion in rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex: amyloid-β1-42-induced reduction of proinsulin level via glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Cell Signal., 26, 253-259 (2014)
- Arimura T, et al. Dilated cardiomyopathy-associated FHOD3 variant impairs the ability to induce activation of transcription factor SRF. Circ. J., 77, 2990-2996 (2013)
- Nemoto T, et al. Involvement of the orexin system in adrenal sympathetic regulation. Pharmacology, 91, 250-258 (2013)
- Nemoto T, et al. Endothelin-1-induced down-regulation of NaV1.7 expression in adrenal chromaffin cells: attenuation of catecholamine secretion and tau dephosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 587, 898-905 (2013)
- Kan-o M, et al. Mammalian formin Fhod3 plays an essential role in cardiogenesis by organizing myofibrillogenesis. Biol. Open, 1, 889-896 (2012)
- Kan-o M, et al. Expression and subcellular localization of mammalian formin Fhod3 in the embryonic and adult heart. PLoS ONE, 7, e34765 (2012)