Summary
The actin cytoskeleton is vital for a number of biological processes, including morphogenesis, motility, polarity establishment, and modulation of mechanical stress. These various tasks are performed by precise spatio-temporal control of actin polymerization/depolymerization dynamics. However, little is known about the regulatory mechanisms of actin assembly in these processes in vivo. We use a multi-disciplinary approach that combines genetics, biochemistry, histology, and pharmacology to study these problems from the molecular to organism level.
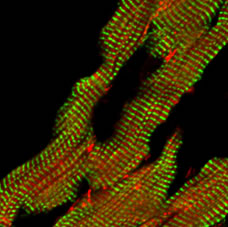
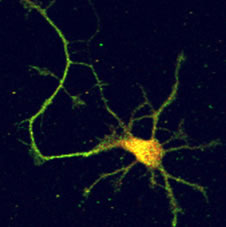
Research Projects
- Actin assembly mechanisms
- Actin dynamics in cardiomyocytes and non-muscle cells
Lab Techniques

- Basic molecular biology techniques
- Basic techniques for mammalian cell culture
- Maintenance and handling of genetically modified mice
- Expression and purification of recombinant proteins
- Primary culture of cardiomyocytes and neurons
- Morphological and histological observation techniques
Publications
- Syaban MFR, et al. Structural basis underlying the autoinhibition of the formin FHOD1 and its phosphorylation-dependent activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2026; 302: 111109. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.111109.
- Nakagawa H, et al. The expression of the formin Fhod3 in mouse tongue striated muscle. Cell Struct. Funct., 2024; 49: 111-122. doi: 10.1247/csf.24044.
- Sakata K, et al. Differential effects of the formin inhibitor SMIFH2 on contractility and Ca2+ handling in frog and mouse cardiomyocytes. Genes Cells. 2021; 26:583-595. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12873.
- Sulistomo HW, et al. Fhod3 controls the dendritic spine morphology of specific subpopulations of pyramidal neurons in the mouse cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex 2021;31:2205–2219. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa35
- Sanematsu F, et al. Fhod1, an actin-organizing formin family protein, is dispensable for cardiac development and function in mice. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Feb;76(2):219-229. doi: 10.1002/cm.21523.
- Matsuyama S, et al. Interaction between cardiac myosin-binding protein C and formin Fhod3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 ; 115: E4386-95. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716498115.
- Sulistomo HW, et al. Formin homology 2 domain-containing 3 controls neural plate morphogenesis in mouse cranial neurulation by regulating multidirectional apical constriction. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294: 2924-2934.
- Ushijima T, et al. The actin-organizing formin protein Fhod3 is required for postnatal development and functional maintenance of the adult heart in mice. J Biol Chem. 2018; 293:148-162.
- Kan-o M, et al. Mammalian formin Fhod3 plays an essential role in cardiogenesis by organizing myofibrillogenesis. Biol. Open 2012; 1: 889-896.
- Taniguchi K, et al., Mammalian Formin Fhod3 Regulates Actin Assembly and Sarcomere Organization in Striated Muscles. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284: 29873-29881.
- Takeya R, et al. The mammalian formin FHOD1 is activated through phosphorylation by ROCK and mediates thrombin-induced stress fibre formation in endothelial cells. EMBO J 2008; 27: 618-628.