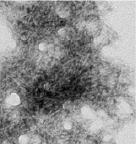
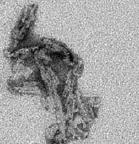
Summary
Our primary research interest focuses on the molecular basis of neurodegenerative diseases due to abnormal aggregation of protein, including Prion diseases (PrD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and Alzheimer disease (AD). We recently established a highly sensitive cell-free prion conversion assay, designated “real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QUIC),” for detection of a tiny amount of prion in the samples. Accumulating evidence showed that this assay is useful for the diagnosis and drug screening for PrD. By developing the principal of the cell-free protein conversion assay, we would like to establish the diagnostic method for other neurodegenerative diseases, especially DLB and AD. Furthermore, we also investigate the development of effective drugs for PrD, DLB, and AD.
Research Projects
- Development of highly sensitive diagnostic assay for Neurodegenerative diseases
- Novel drug screening for prion diseases and Alzheimer diseases
- Molecular basis of prion formation and prion strain phenomenon
- The origin of biological homochirality
Laboratory Techniques
- Basic techniques for molecular biology, biochemistry, cell biology, and microbiology
- Conformational analysis of protein (e.g. FTIR, CD, Thermal stability assay)
International Collaboration
- TSE/Prion Biochemistry Section, Laboratory of Persistent Viral Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health
- The National CJD Research and Surveillance Unit, University of Edinburgh
- Department of Pathology, Mental Health Research Institute of Victoria, The University of Melbourne
Publications
- McGuire LI, Poleggi A, Poggiolini I, Suardi S, Grznarova K, Shi S, de Vil B, Sarros S, Satoh K, Cheng K, Cramm M, Fairfoul G, Schmitz M, Zerr I, Cras P, Equestre M, Tagliavini F, Atarashi R, Knox D, Collins S, Haïk S, Parchi P, Pocchiari M, Green A. CSF RT-QuIC is a robust and reliable test for sporadic CJD: An international study. Ann Neurol. 2016 Apr 30.
- Mori T, Atarashi R, Furukawa K, Takatsuki H, Satoh K, Sano K, Nakagaki T, Ishibashi D, Ichimiya K, Hamada M, Nakayama T, Nishida N. A direct assessment of human prion adhered to steel wire using real-time quaking-induced conversion. Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 26;6:24993.
- Takatsuki H, Satoh K, Sano K, Fuse T, Nakagaki T, Mori T, Ishibashi D, Mihara B, Takao M, Iwasaki Y, Yoshida M, Atarashi R, Nishida N. Rapid and Quantitative Assay of Amyloid-Seeding Activity in Human Brains Affected with Prion Diseases. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 12;10(6):e0126930.
- Sano K, Atarashi R, Ishibashi D, Nakagaki T, Satoh K, Nishida N. Conformational properties of prion strains can be transmitted to recombinant prion protein fibrils in real-time quaking-induced conversion. J Virol. 2014 Oct;88(20):11791-801.
- Nakagaki T, Satoh K, Ishibashi D, Fuse T, Sano K, Kamatari YO, Kuwata K, Shigematsu K, Iwamaru Y, Takenouchi T, Kitani H, Nishida N, Atarashi R. FK506 reduces abnormal prion protein through the activation of autolysosomal degradation and prolongs survival in prion-infected mice. Autophagy. 2013 Sep;9(9):1386-94.
- Sano K, Satoh K, Atarashi R, Takashima H, Iwasaki Y, Yoshida M, Sanjo N, Murai H, Mizusawa H, Schmitz M, Zerr I, Kim YS, Nishida N. Early detection of abnormal prion protein in genetic human prion diseases now possible using real-time QUIC assay. PLoS One.
- Ishibashi D, Atarashi R, Fuse T, Nakagaki T, Yamaguchi N, Satoh K, Honda K, Nishida N. Protective role of interferon regulatory factor 3-mediated signaling against prion infection. J Virol. 2012 May;86(9):4947-55.2013;8(1):e54915.
- Atarashi R, Satoh K, Sano K, Fuse T, Yamaguchi N, Ishibashi D, Matsubara T, Nakagaki T, Yamanaka H, Shirabe S, Yamada M, Mizusawa H, Kitamoto T, Klug G, McGlade A, Collins SJ, Nishida N. Ultrasensitive human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid by real-time quaking-induced conversion. Nat Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):175-8.